My Garage
My Account
Cart
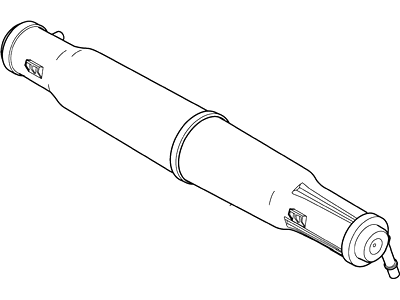
Genuine Ford Ranger Vapor Canister
Fuel Vapor Canister- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
12 Vapor Canisters found
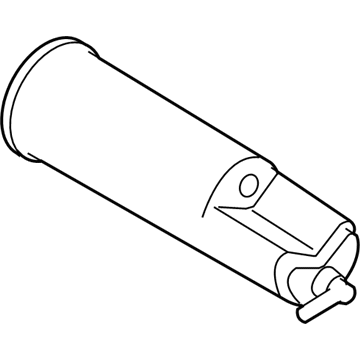
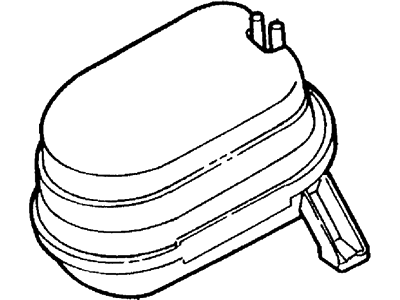
Ford Ranger Reservoir Assembly
Part Number: F75Z-9D653-AC$163.90 MSRP: $270.91You Save: $107.01 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Ranger Cannister - Fuel Vapour Store
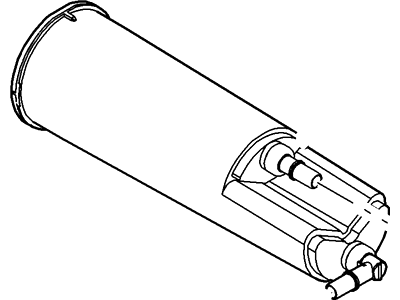
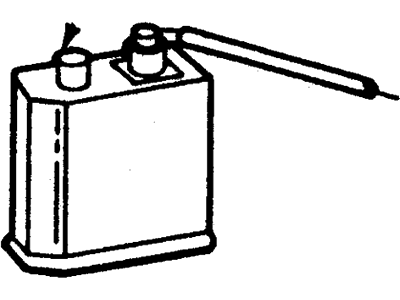
Part Number: 4L5Z-9C985-B$239.56 MSRP: $385.45You Save: $145.89 (38%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysFord Ranger Cannister - Fuel Vapour Store
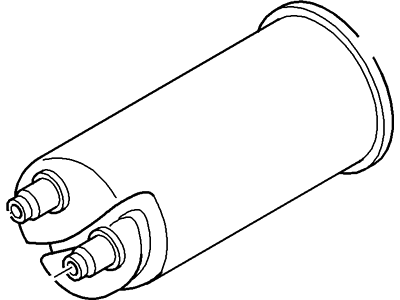
Part Number: 4L5Z-9C985-AA$137.94 MSRP: $220.00You Save: $82.06 (38%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysFord Ranger Cannister - Fuel Vapour Store
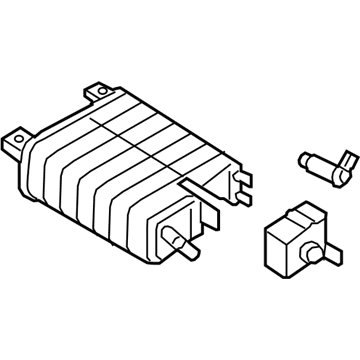
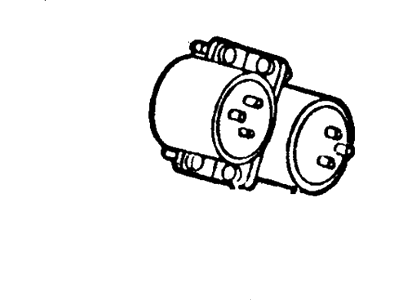
Part Number: GD9Z-9D653-A$280.92 MSRP: $452.00You Save: $171.08 (38%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Ford Ranger Vapor Canister
Vapor Canister in Ford Ranger vehicle is applicable part of the EVAP or evaporative emissions control system developed to ensure that HC or hydrocarbon evaporative emissions should not find their way to the atmospheric environment. It works in as much as it holds fuel vapours from the fuel tank and expels them into the combustion chamber for burning as a part of the airstream/fuel mixture. It is controlled by a purge valve that is activated when the engine is on, and a vacuum then pulls in the air and the vapor from the canister. For several years, several types of Vapor Canisters have been incorporated in different models of the Ranger, including a filter that may be replaced to regulate saturation. In the more recent OBD II systems, there is a new element of the canister vent solenoid and fuel tank pressure sensor to improve diagnostics, and check for leaks. They have ensured that the canister of vapor maximizes the extent of emitting pollutants while at the same time enhancing the performance of the vehicles on the road.
We provide a wide range of Ford Ranger Vapor Canister at the best prices possible. If you need Ford Ranger Vapor Canister, you can shop with confidence on our website. All our OEM parts come with a manufacturer's warranty and are delivered to your door step with a fast delivery service.
Ford Ranger Vapor Canister Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What is the purpose of the Evaporative Emissions Control (EVAP) system and Canister on 1993-2011 Ford Ranger?A:To begin with, the EVAP system is responsible for keeping the fuel vapor from escaping into the atmosphere. Some of the parts of the system include the EVAP canister, fuel tank pressure sensor, fuel vapor vent valve, canister vent solenoid, fuel filler pipe check valve, canister purge valve and EVAP dust separator. The canister stores fuel vapors while the pressure sensor monitors tank pressure. The vent valve prevents overfilling and solenoid controls vapor flow. The check valve blocks fuel escape during refuelings. The purge valve regulates vapour flow to intake manifold. Dust separator prevents entry of particles into the system. Common symptoms include poor engine performance and gas smells in particular cases concerning EVAP faults. Inspection and component replacement may be necessary after a professional diagnosis using an OBD-II scan tool.
- Q: What is the purpose of the Evaporative Emissions Control (EVAP) system and Vapor Canister on 2000-2011 Ford Ranger?A:The Evaporative Emissions Control (EVAP) system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. On warm days, these vapors expand and are routed to the EVAP canister for temporary storage. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) then allows these vapors to be drawn into the engine. The EVAP canister, located under the vehicle, contains activated charcoal and requires no maintenance. Other key components include the fuel tank pressure sensor, fuel vapor vent valve, and canister vent solenoid. Symptoms of a faulty EVAP system include a strong fuel smell and poor driveability. Diagnosis and repair should be done with an OBD-11 scan tool and by a qualified repair shop. Component replacement involves detaching vacuum lines and replacing the canister.
Related Ford Ranger Parts
Browse by Year
2023 Vapor Canister 2022 Vapor Canister 2021 Vapor Canister 2020 Vapor Canister 2019 Vapor Canister 2011 Vapor Canister 2010 Vapor Canister 2009 Vapor Canister 2008 Vapor Canister 2007 Vapor Canister 2006 Vapor Canister 2005 Vapor Canister 2004 Vapor Canister 2003 Vapor Canister 2002 Vapor Canister 2001 Vapor Canister 2000 Vapor Canister 1999 Vapor Canister 1998 Vapor Canister 1997 Vapor Canister 1996 Vapor Canister 1995 Vapor Canister 1994 Vapor Canister 1993 Vapor Canister 1992 Vapor Canister 1991 Vapor Canister 1990 Vapor Canister 1989 Vapor Canister 1988 Vapor Canister 1987 Vapor Canister 1986 Vapor Canister 1985 Vapor Canister 1984 Vapor Canister 1983 Vapor Canister