My Garage
My Account
Cart
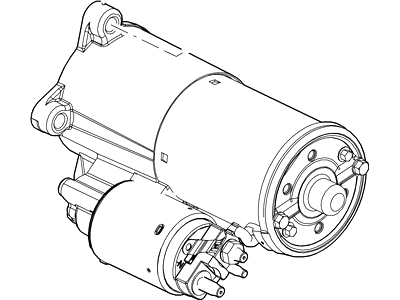
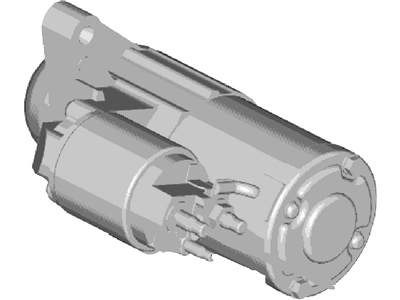
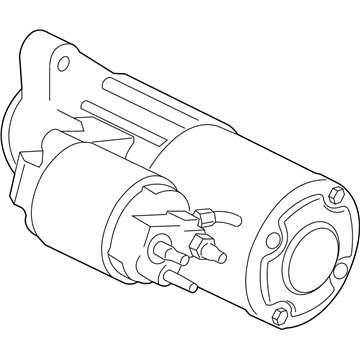
Genuine Ford Mustang Starter
Starter Ignition- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
38 Starters found
Ford Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: 9L3Z-11002-A$157.66 MSRP: $254.55You Save: $96.89 (39%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: CK4Z-11002-A$155.84 MSRP: $256.36You Save: $100.52 (40%)Ford Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: CK4Z-11002-C$166.84 MSRP: $274.55You Save: $107.71 (40%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: F7UZ-11002-AARM$147.59 MSRP: $238.18You Save: $90.59 (39%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: GR3Z-11002-A$332.10 MSRP: $552.73You Save: $220.63 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: F7SZ-11002-AARM$136.74 MSRP: $230.91You Save: $94.17 (41%)Ford Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: FR3Z-11002-C$241.63 MSRP: $401.82You Save: $160.19 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: FR3Z-11002-B$241.63 MSRP: $401.82You Save: $160.19 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: 6R3Z-11002-A$154.53 MSRP: $254.55You Save: $100.02 (40%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: CR3Z-11002-A$241.63 MSRP: $401.82You Save: $160.19 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: F7UZ-11V002-AARM$147.59 MSRP: $238.18You Save: $90.59 (39%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: FR3Z-11002-D$179.72 MSRP: $285.45You Save: $105.73 (38%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: FR3Z-11002-A$146.65 MSRP: $236.36You Save: $89.71 (38%)Ford Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: BR3Z-11002-A$155.84 MSRP: $256.36You Save: $100.52 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: CK4Z-11002-B$166.84 MSRP: $274.55You Save: $107.71 (40%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: 7R3Z-11002-A$139.91 MSRP: $230.91You Save: $91.00 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: HU2Z-11V002-CBRM$135.42 MSRP: $218.18You Save: $82.76 (38%)Ships in 1 Business DayFord Mustang Starter Motor Assembly
Part Number: 5R3Z-11002-A$154.53 MSRP: $254.55You Save: $100.02 (40%)Ships in 1 Business Day
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 38 Results
Ford Mustang Starter
The Ford Mustang Starter is one of those parts that help to transform electrical current from the battery into mechanical force to start the engine. This process is started externally with the help of a solenoid that is fixed with the battery and starts the motor. Starter consist of rotating armature that works in conjunction with field coils or permanent magnets to provide necessary rotation that connects the drive of the starter and the engine flywheel or flexplate ring gear. Yearly, different models of Ford Mustang have been associated with different starters, they include gear reduction starts which employs a reduction gear. These starters are especially used for high compression engines because these engines need more hard wearing as well as efficient starters compared to the standard OEM starters. As discussed earlier, OE starters provide a high amount of initial torque, but this is a problem when used for kickback or failure when charging high-compression engines. Lastly, I'd like to make a conclusion that the Ford Mustang Starter is an indispensable tool that guarantees the engine will start. It has developed more effective designs such as gear-reduction systems to cater for the latest high-performance engine needs thus underlining its role in the performance of the car.
We provide a wide range of Ford Mustang Starter at the best prices possible. If you need Ford Mustang Starter, you can shop with confidence on our website. All our OEM parts come with a manufacturer's warranty and are delivered to your door step with a fast delivery service.
Ford Mustang Starter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What should you check if a malfunction occurs in the starting circuit and Starter on Ford Mustang?A:If a malfunction occurs in the starting circuit, do not immediately assume that the starter is causing the problem; first, check that the Battery Cable clamps are clean and tight at the battery terminals, inspect the condition of the battery cables and replace any defective ones, test the battery's condition and replace it if it does not pass all tests, inspect the starter solenoid wiring and connections, ensure the starter mounting bolts are tight, verify that the starter is receiving voltage on the S terminal of the starter solenoid when the ignition key is turned to Start, and check the operation of the Digital Transmission Range sensor or clutch start switch to ensure proper function. If the starter does not actuate when the ignition switch is turned to the START position, check for battery voltage at the solenoid using a test light or voltmeter. If there is no voltage, check the ignition switch fuse and starter relay; if there is voltage but the starter motor does not operate, remove the starter and bench test it. If the starter turns over slowly, check the starter cranking voltage and current draw from the battery, ensuring the voltage does not drop below specified levels and that the current draw remains within the correct range. If the starter is getting voltage but doesn't operate, remove the starter/solenoid assembly and test it on the bench, checking for solenoid defects or potential engine seizure. When testing, connect jumper cables to the starter and apply battery voltage to the solenoid S terminal, observing the movement of the solenoid plunger and pinion drive to determine if the starter/solenoid assembly is functioning properly.
Related Ford Mustang Parts
Browse by Year
2024 Starter 2023 Starter 2022 Starter 2021 Starter 2020 Starter 2019 Starter 2018 Starter 2017 Starter 2016 Starter 2015 Starter 2014 Starter 2013 Starter 2012 Starter 2011 Starter 2010 Starter 2009 Starter 2008 Starter 2007 Starter 2006 Starter 2005 Starter 2004 Starter 2003 Starter 2002 Starter 2001 Starter